A colonoscopy is an essential test for finding polyps and colorectal cancer. You must prepare for the test by following a special diet and drinking clear liquids for several days. During the trial, doctors insert a long, thin tube with a camera and light (colonoscope) into your anus and rectum and up into your large intestine or colon.
Risk Factors
When a person undergoes a colonoscopy Denver, they will be asked to wear a hospital gown and lie on an examination table. A sedative or other medication will be administered to help them relax. Then, the doctor inserts a thin, flexible colonoscope tube into the rectum and colon (large intestine). The colon is inflated with air or carbon dioxide to get a better view. If any polyps are discovered during the procedure, the doctor will remove them and send them to a lab for testing.
This may cause slight bleeding, but it usually stops quickly, and some gas and bloating might occur. People at a higher risk of colon cancer may be recommended to undergo more frequent screening tests, like a fecal occult blood test or a fecal immunochemical test (FIT). A colonoscopy is more comprehensive than these other tests and can help identify cancer, large polyps, or other abnormalities. People at high risk may also be recommended a flexible sigmoidoscopy.
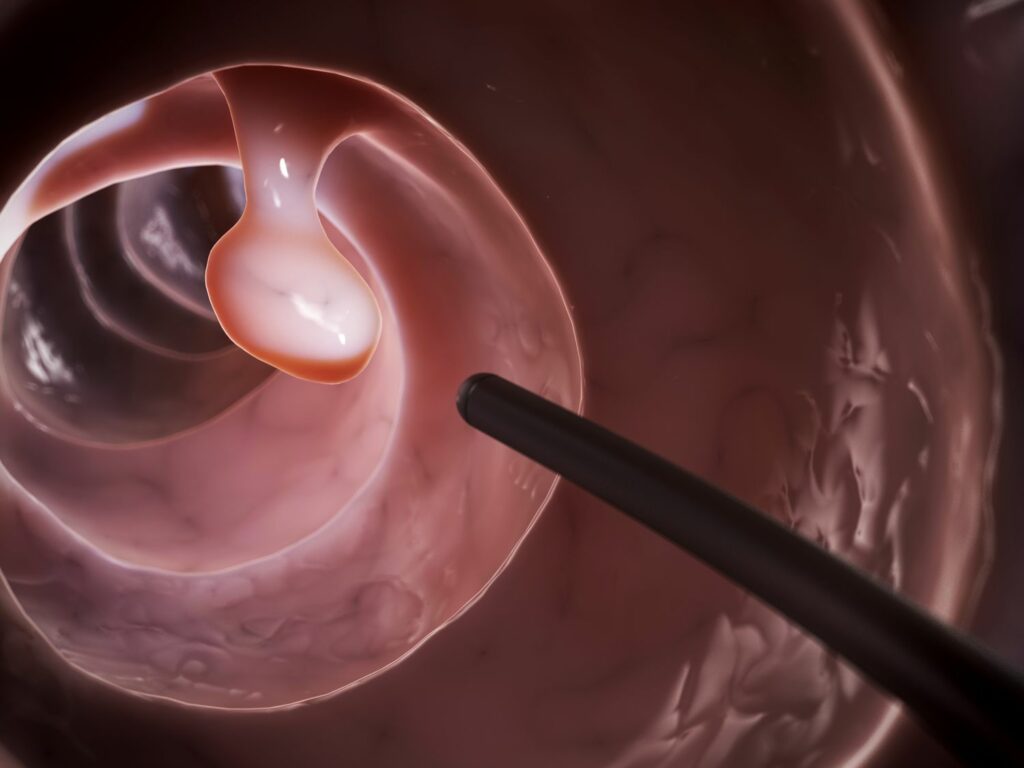
Polyps
Polyps are growths that stick out from the lining of the colon and rectum. They are usually benign, but some types can become cancerous over time. Colon screening removes these pre-cancerous polyps before they can grow larger and cause cancer. Polyps can be categorized as hyperplastic, adenomatous, or villous (adenomas) based on their appearance under the microscope. No specific size determines whether a polyp will turn into cancer, but the more pre-cancerous polyps an individual has, the higher their risk.
Polyps often do not cause symptoms but are diagnosed by a stool test, flexible sigmoidoscopy, or colonoscopy, or if an individual experiences rectal bleeding, a change in bowel habits, or blood in the stools. Polyps can be a variety of shapes and sizes: Sessile polyps are flat or raised on short stalks. Pedunculated polyps appear as small cauliflower or mushrooms that grow on the top of the colon wall. Serrated polyps have saw-toothed edges.
Cancer
You lie on an exam table during a colonoscopy and receive sedation or pain medications. If polyps are found, a pathologist will examine the tissue to see whether it’s cancerous. You may have some bleeding from your anus, which is normal. You may need a low-fiber diet for two or three days before the test. On the day of the colonoscopy, you take a laxative formula that empties your bowels before your procedure. Your doctor will instruct you on what to eat before the test and the day after the colonoscopy. You should arrange for someone to drop you off at the hospital before your test and to drive you home afterward.
Prevention
The most important step is recognizing when something may be wrong, which means regular screenings with colonoscopies. These are painless, quick, and potentially lifesaving. During a colonoscopy, doctors use a camera on the end of a flexible tube (a scope) to examine the lining of your large intestine. The procedure is done in a hospital, doctor’s office, or an outpatient clinic. You lie on the exam table with your knees drawn toward your chest.
The doctor inserts the scope into your anus and up through your rectum and colon. The content is inflated with air or carbon dioxide for a better view. To prepare for the test, you must drink lots of clear liquids starting the day before your procedure. You also must follow a special diet and take laxatives in pill or liquid form.